Learning rules for comparing the activities of Alzheimer's drugs

Contents and links
Alzheimer's disease has long been recognised as one of the most
disabling conditions affecting the aged. It is the major cause of
dementia among elderly people. The drug Tacrine
has drawn considerable
attention because of a report of its clinical efficacy for this problem. Its
structure
is shown here:
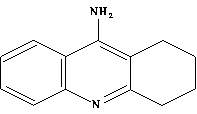
However, large-scale clinical trials show that the primary disadvantage of
Tacrine is its high toxicity. This has led to investigations into
possible variants of the basic Tacrine structure. Some reported
variations
used the following structure
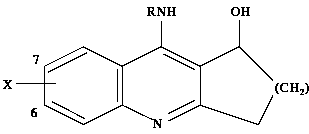
In this structure, new compounds are created by substituting
for R and X, where
the substitution for X can be in position 6 or 7.
The need to guide experimentation
The literature contains many reports of tests on
the properties of new drugs - in the case of Alzheimer's, desirable
proprties include
- Low toxicity.
- High acetocholinesterase inhibition.
- Good reversal of scopolamine induced deficiency.
- Inhibit amine re-uptake.
However, these reports do not indicate any particular pattern followed in
creating these new drugs. The aim of our research is to learn rules that tell
us what makes a drug have a desirable property (for example, low
toxicity). Hopefully, these rules will offer better guidance for
the synthesis of new drugs.
Using ILP to learn drug properties
In our experiments, data from the chemical literature was converted into a representation suitable for ILP, as described in
[King, R.D., Srinivasan, A. and Sternberg, M.J.E.(1995)].
The chemical data itself is taken from
[Shutske G.M. et al(1989)].
In the dataset provided here,
rules are to be learnt for each property using the
following information:
- The positive and negative examples are pairwise comparisons
of drugs. There are different sets of examples for each
property.
- Physical and chemical properties of chemicals that can be substituted for
R or X.
These are described by unary predicates in the background knowledge.
These properties include hydrophobicity, hydrophilicity,
charge, size, polarity, whether a chemical is aliphatic or aromatic, whether
it is a hydrogen donor or acceptor etc.
- Sizes, hydrophobicities, polarities etc., are represented by constants
such as
polar0 and polar1.
- Relations between the constant, expressed as
clauses such as
less_than(polar0,polar1), are
also provided as background knowledge.
x_subst(Drug,Position,Subs). The X substitution for Drug in
position Position is Subs.
- The R substitution is split into parts corresponding to bonds
between different chemical structures.
- Sometimes the R substitution involves the presence of 1 or more
ring structures. These are benzyl derivatives that arise from
substitutions within the basic benzene ring structure. The number
of such substitutions in the basic benzene structure, the position
of the substitutions an the actual substituent are provided.
The data used in these experiments is contained in
one compressed TAR file.
Bibliography
King, R.D., Srinivasan, A. and Sternberg, M.J.E. (1995).
Relating chemical activity to structure: an examination of ILP successes.
New Gen. Comput. (to appear).
Shutske G.M., Pierrat F.A., Kapples K.J., Cornfeldt M.L.,
Szewczak M.R., Huger F.P., Bores G.M., Haroutunian V. and Davis K.L. (1989).
9-Amino-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridin-1-ols: Synthesis and Evaluation as Potential
Alzheimer's Disease Therapeutics.
Up to applications main page.
 Machine Learning Group Home Page
Machine Learning Group Home Page



 Machine Learning Group Home Page
Machine Learning Group Home Page