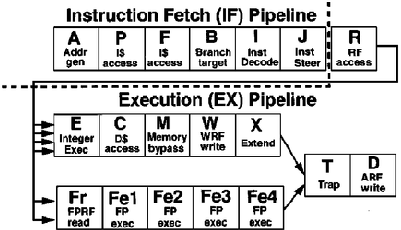
 |
Stage Function
A Generate instruction fetch addresses, generate predecoded
instruction bits on cache fill
P Fetch first cycle of instructions from cache; access first cycle
of branch prediction
F Fetch second cycle of instructions from cache; access second
cycle of branch prediction; translate virtual-to-physical address
B Calculate branch target addresses; decode first cycle of instructions
I Decode second cycle of instructions; enqueue instructions into the queue
J Steer instructions to execution units
R Read integer register file operands; check operand dependencies
E Execute integers for arithmetic, logical, and shift instructions;
read, and check dependency of, first cycle of data cache access
floating-point register file
C Access second cycle of data cache, and forward load data for word
and double-word loads; execute first cycle of floating-point instructions
M Load data alignment for half-word and byte loads; execute second
cycle of floating-point instructions
W Write speculative integer register file; execute third cycle of
floating-point instructions
X Extend integer pipeline for precise floating-point traps; execute
fourth cycle of floating-point instructions
T Report traps
D Write architectural register file
Table 1 : UltraSPARC-III Pipeline stages and their functionalities
One problem that can occur with a deep pipeline is that the cost of
a branch misprediction is very high as we have to flush the whole pipeline
and start fetching from stage A again. This means that we incur a penalty of
eight cycles (A through E stage). This is indeed a heavy penalty to pay, the
design has taken this into consideration and there is an implementation of
a miss queue, which has all the instructions that were fetched during the
predict taken phase, but was on the other path. These instructions will be
immediately available to start the I stage. This will be dealt in more
detail when we talk about the instruction issue unit.
There are six major functional units : instruction issue unit (IIU),
floating point unit (FPU), integer execution unit (IEU), data cache unit
(DCU), external interface unit (EIU), and system interface unit (SIU). These
are explained in much greater detail below: